In a world of uncertain electric power, backup power options keep the lights on, the family warm, and the food safe.
Aging and Outdated Infrastructure Cause Nearly Half of All Outages and Blackouts
Following the rural electrification project that began in the 1930s, accessible electrical power completed the transition from luxury to convenience and started the country down a road to necessity. The United States built most of the national power transmission and distribution grid in the 1950s and 1960s with an expected life of 50 years. Considering the available technology in that era, rural electrification and a national power grid were phenomenal accomplishments. The country progressed from lighting a few homes and businesses with Thomas Edison’s first electric utility in 1882 to powering an entire nation and enabling a myriad of new appliances and conveniences.
It’s an unfortunate fact that our national transmission and distribution system has aged and deteriorated beyond its original expected lifetime.
140 years after the Edison Illuminating Company turned on the lights, the power grid becomes increasingly frail with every passing year. Expensive upgrades cost billions. Expenditures on grid improvements average about 20-billion dollars a year. According to a report by the American Society of Civil Engineers, the United States faces a 340 billion-dollar shortfall in grid infrastructure improvements by 2039. Many states focus on adding renewable wind and solar energy and give less importance to infrastructure upgrades in favor of reducing carbon emissions. In the meantime, the grid continues to age. As a result, reliability suffers.
Severe weather accounts for about 50 percent of all outages. In 2019, unexpected interruptions in transmission and distribution or equipment failures caused 46 percent of all outages and blackouts.
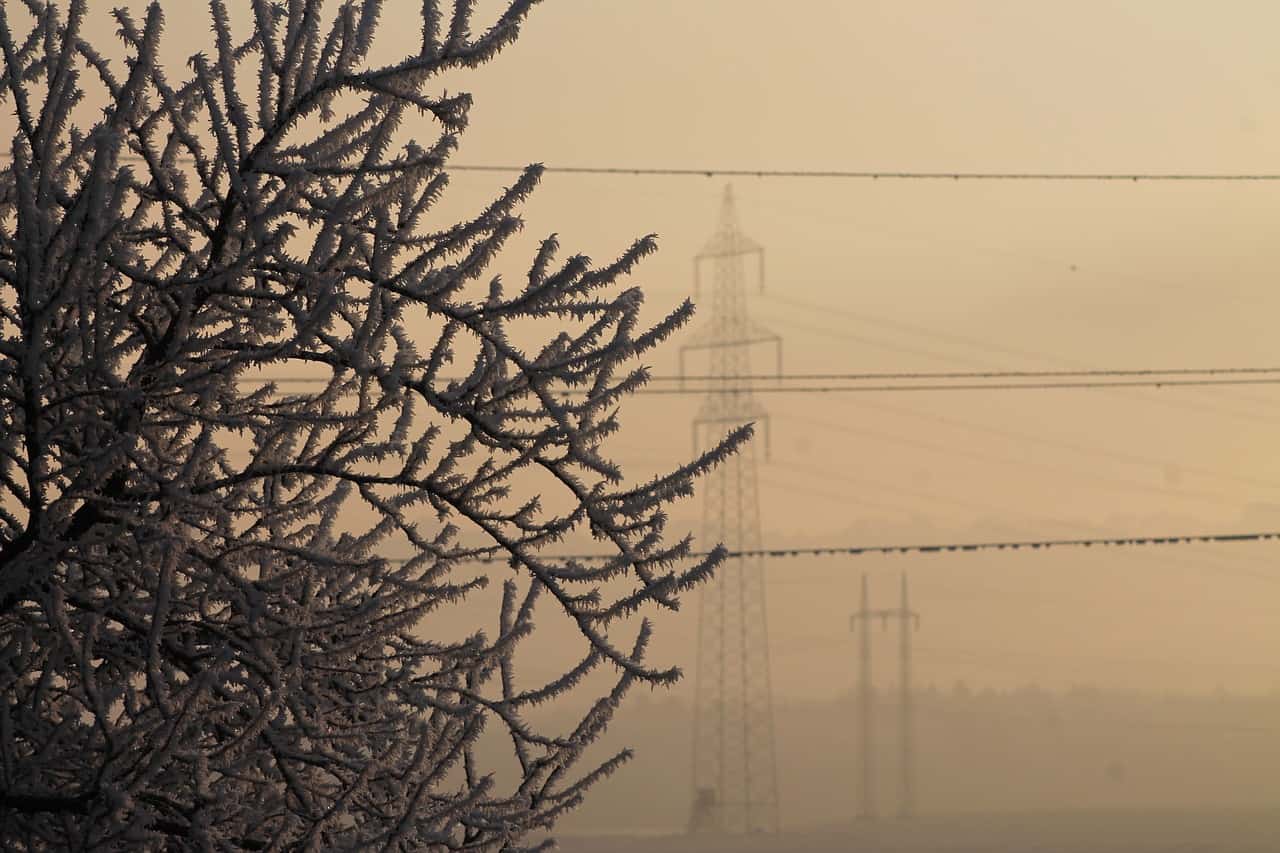

Ice hangs from power lines as it accumulates during a winter storm. Lines can snap as they become too heavy or break when trees topple or break under the heavy ice.
Power Outage Preparation
With the expected shortfall in distribution-transmission and the worsening effects of severe weather on the grid, consumers can expect more outages and blackouts.
Preparation with an alternative backup power source ensures the refrigerator runs and the lights work when the utility can’t deliver power. Today, we have more options than ever with solar power and battery storage. Home backup generators are quieter, more fuel efficient, more powerful, and they meet stringent air quality guidelines. Portable generators are affordable and not automatic. Standby Generators manage power and keep the whole house working, if that’s what you need.
A severe storm followed by a power outage sends hundreds of utility customers to the home centers and hardware stores for a portable generator. Early shoppers are successful, but don’t always get what they need and must take whatever the store has available.
A better way prepares for an outage before it happens. Determine power requirements, what type of backup power does the job most efficiently, and then invest in a quality backup system.
Backup Power Options
- Backup Generator: Any generator used to supply power during an outage or blackout.
- Standby Generator: Fully automatic startup. Power a home or business for days or weeks in any weather, including hurricanes.
- Portable Generator: Not automatic. Needs frequent refueling. Must be set up and connected before each use.
- Solar + Battery Storage: Solar cells produce electricity in the sunshine. Batteries store power from the grid or solar array.
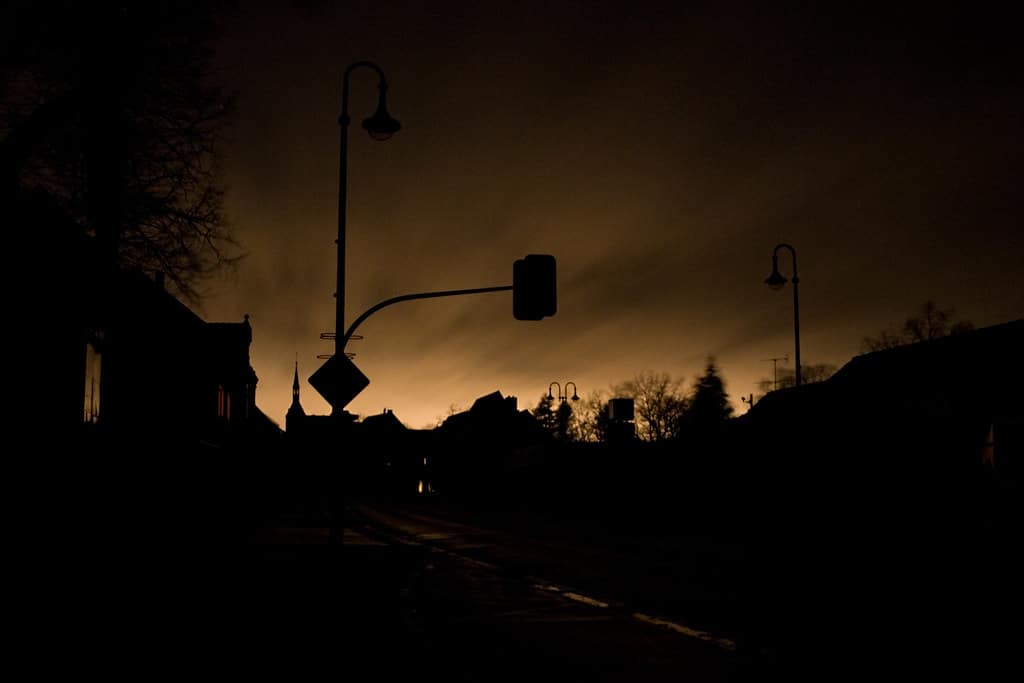

City streets, homes, businesses, and traffic signals are dark during a power outage.
Solar Power + Storage
A solar array with battery storage brings the latest technology and the most solar power options to the modern home or businesses.
Batteries store energy from one or more power sources for future use including solar arrays, backup generators, wind turbines, and even the electric utility.
Sunny days produce the most power. Partly cloudy and overcast periods lower power output. The inverter stores energy from the array in the batteries or it converts it for use by the home or business. Fully charged batteries allow the inverter to add electricity from the solar array directly to the electrical system to reduce power use from the grid.
Good design allows a solar + battery storage system to power a home or business during a power outage or blackout. Generac PWRcell offers multiple modes of operation. The usual installation includes a solar array, but the batteries can operate as stand-alone storage. The battery cabinets charge from the utility. With the solar array, the house runs on solar during the day and battery power at night.
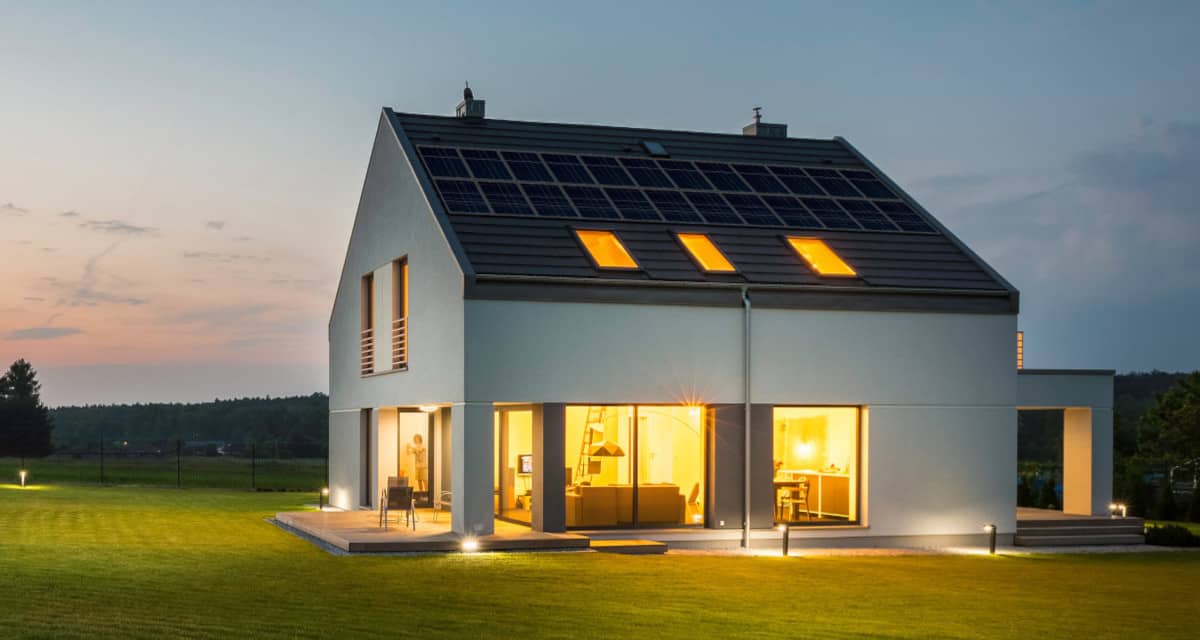

This solar home has lights after the sun goes down. Batteries charged during the day power the home after sunset.
Battery Storage
Battery technology has improved into a cost-effective energy storage medium capable of holding more energy in less space for less money. The Generac PWRcell Battery Storage with PWRcell Inverter scales from 9 kilowatt-hours to 36 kilowatt-hours with a maximum current of 50 amps. Enough to power lights, refrigerator, and all the usual comforts including a mid-sized central air conditioner.
Without a Solar Array, Generac PWRcell Components charge the batteries from the utility for use during a power outage or blackout, or during higher rate periods.
The PWRcell inverter connects with the PWRview Mobile App, which allows the homeowner or business operator to monitor energy use in real time. Informed about they use energy, PWRview users can change energy-use habits for significant savings.
Generac PWRcell uses Smart Management Modules to lock out heavy loads that would overload the system or drain the batteries. Other heavy loads run based on priority and available power. Well pumps are essential. Electric dryers and pool heaters are convenience or luxury items and locked out during an outage in most cases.
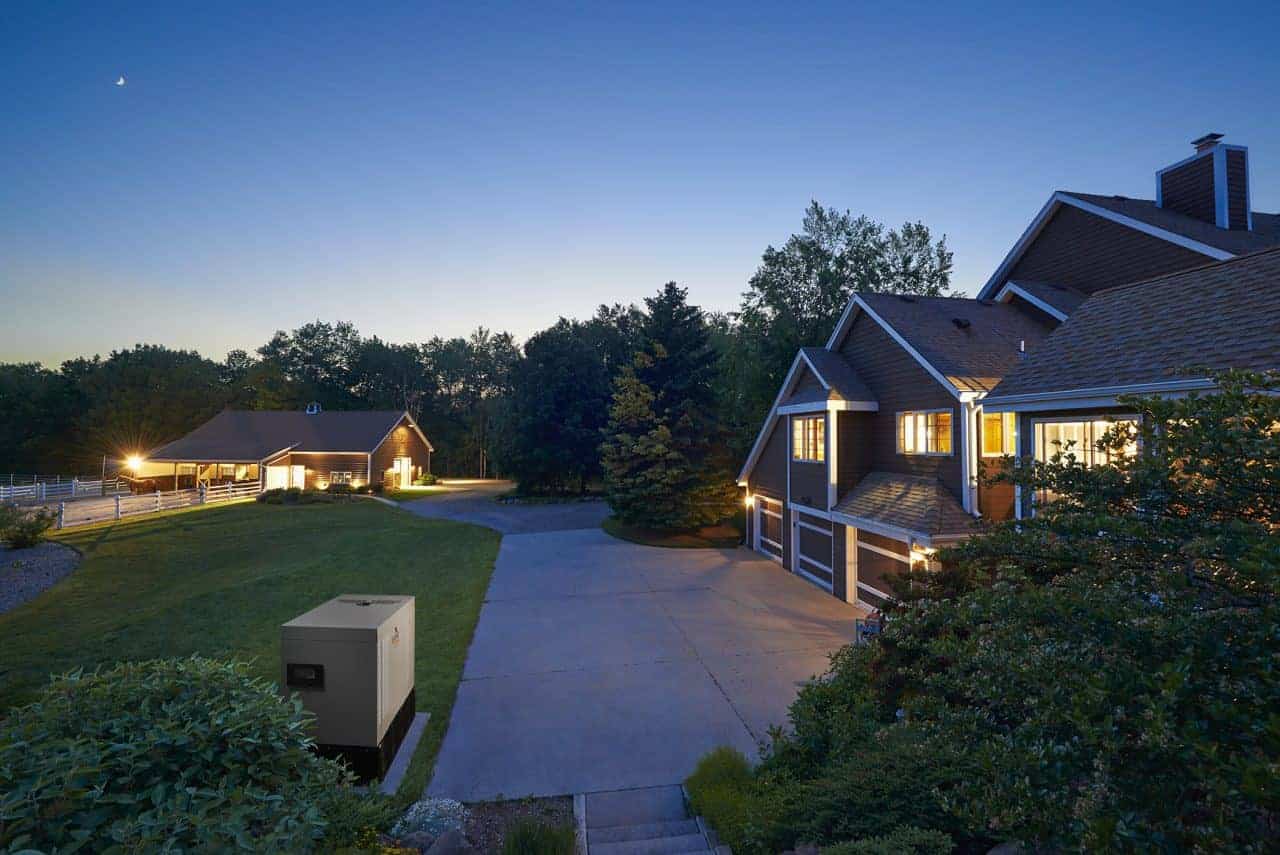
This Generac Protector Standby Generator Keeps the House and Barn Powered During an Outage
Standby Generator
Of all the proven technologies, an automatic standby generator covers all the bases. They start and run in any weather, including hurricanes. Natural gas or propane allow them to run for long periods following natural disasters or during blackouts. Night or day, a continuous supply of fuel keeps the generator running for weeks with regular care and maintenance.
Best Natural Gas Home Standby Generators
Propane installations need an appropriately sized storage tank and arrangements for delivery during outages lasting more than one or two weeks. Diesel generators have integrated tanks for up to three days of run time. Additional onsite storage extends the run time.
From 7.5kW to 150kW, a backup generator for home or business can power a few essential circuits, supply large or luxury homes and estates, or restore power to businesses and farms to keep them open and operating.

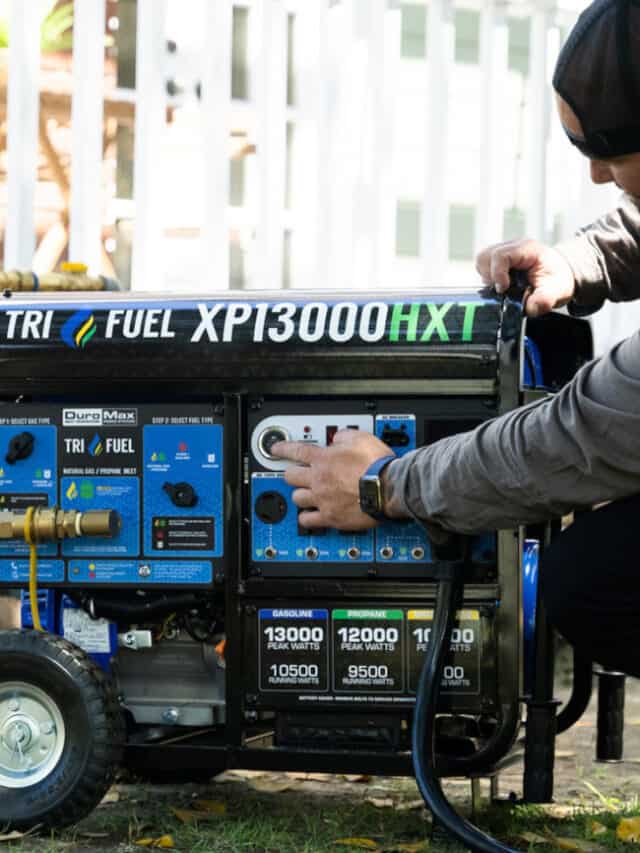
A Portable Generator can power your lights and a few appliances, but it can’t power the entire home.
Portable Generator
Ask any forum or social media group what size generator you need, invariably you’ll get several answers stating that a 2000 to 3000-watt generator is all you need. Power your fridge, turn on a few lights. Charge up the cell phone. It even sounds charming in a rustic, minimalist kind of way—until you try to get by for a week.
3000 watts is less power than two household outlets on different circuit breakers, and a little more than one outlet in a modern kitchen. 2000 watts is about equal to a single,15-amp outlet. Is that enough?
Step up to 5000-7000 watts and it becomes more practical for outages longer than a few hours. The big upsides are lower initial cost, and you won’t need a permit or electrical upgrades to use one with extension cords. Poor advice from the internet will advise you to make a homemade cord with two male ends to run your entire house. This is dangerous, and in most places, illegal.
Portable Generator Safety Rules to Live By
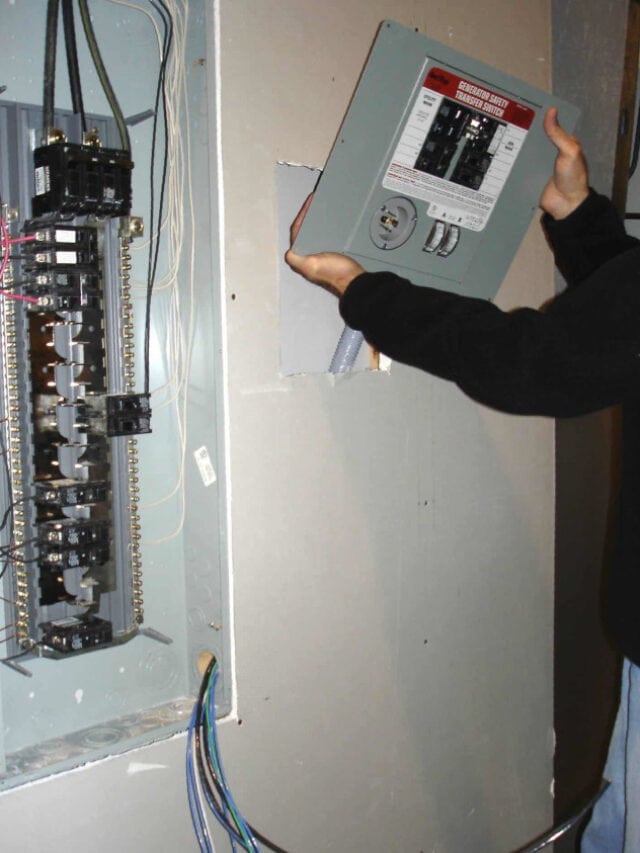
To operate the furnace and other hard-wired appliances, install a manual transfer switch. If you’ve worked with subpanels in the past, you could even do it yourself. Hire an electrician if you have any doubt at all.
Portable Generator downsides include a steady diet of gasoline or propane tanks, a shorter maintenance interval, and they won’t run automatically if you happen to be at work or on vacation when the power goes out. If a big storm knocks out power for the entire community, you might have trouble buying fuel.
A 5000-watt generator can start and run a furnace, refrigerator, freezer, and microwave, with enough power left for a few electronics and lights. Manage power for the coffee maker, hair dryer or curling iron, and similar appliances that generate heat by disconnecting other appliances while you use them.